设置长宽
块级标签设置长宽
'''
块级标签的宽度默认占浏览器一整行,默认情况下,块级标签的高度由标签内容决定,但可以利用 CSS 样式调整块级标签的高度和宽度
'''
<head>
<style>
.d1 {
background: red;
}
.d2 {
background: yellowgreen;
height: 200px;
width: 100px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="d1">123</div>
<div class="d2">123</div>
</body>
行内标签设置长宽
'''
行内标签的高度和宽度由标签内容决定,CSS 调整宽度和高度后不会报错,但浏览器不会执行该内容
'''
<head>
.s1 {
background: red;
}
.s2 {
background: yellowgreen;
height: 200px;
width: 100px;
}
</head>
<body>
<span class="s1">456</span>
<span class="s2">456</span>
</body>
代码演示
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<style>
.d1 {
background: red;
}
.d2 {
background: yellowgreen;
height: 200px;
width: 100px;
}
.s1 {
background: red;
}
.s2 {
background: yellowgreen;
height: 200px;
width: 100px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="d1">123</div>
<div class="d2">123</div>
<span class="s1">456</span>
<span class="s2">456</span>
</body>
</html>
演示结果

字体属性
字体样式
.p1,.p2 {
/* font-family 代表的是字体样式,即选择什么字体,可以输入多个字体,如果浏览器没有第一个字体,就自动使用第二个字体 */
font-family: "Bitstream Vera Sans Mono", Monaco, "Courier New", Courier, monospace;
}
字体大小
.p4 {
font-size: 48px;
}
字体颜色
.p3 {
/* 字体颜色 */
color: red;
/*颜色编号*/
/*color: #eeeeee;*/
/*三原色 数字 范围 0~255*/
/*color: rgb(128,23,45);*/
/*第四个参数是透明度,0~1*/
color: rgb(252, 252, 252);
}
字体粗细
.p5 {
/* 字体粗细 */
/* 加粗 */
font-weight: bolder;
/*boloder light 100-900 inherit继承父元素的标签值*/
}
.p6 {
/* 字体粗细 */
/* 细体 */
font-weight: lighter;
}
.p7 {
/* 字体粗细 */
/* 字体斜体 */
font-style: italic;
}
代码演示
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<style>
.p1,.p2 {
/* font-family 代表的是字体样式,即选择什么字体,可以输入多个字体,如果浏览器没有第一个字体,就自动使用第二个字体 */
font-family: "Bitstream Vera Sans Mono", Monaco, "Courier New", Courier, monospace;
}
.p3 {
/* 字体颜色 */
color: red;
}
.p4 {
font-size: 48px;
}
.p5 {
/* 字体粗细 */
/* 加粗 */
font-weight: bolder;
}
.p6 {
/* 字体粗细 */
/* 细体 */
font-weight: lighter;
}
.p7 {
/* 字体粗细 */
/* 字体斜体 */
font-style: italic;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<p class="p1">奥特曼</p>
<p class="p2">aoteman</p>
<p class="p3">奥特曼</p>
<p class="p4">奥特曼</p>
<p class="p5">奥特曼</p>
<p class="p6">奥特曼</p>
<p class="p7">奥特曼</p>
</body>
</html>
演示结果

文字属性
对齐方式
.p1 {
/* 对齐方式 */
/* 居中 */
text-align: center;
}
.p2 {
/* 对齐方式 */
/* 右对齐 */
text-align: right;
}
.p3 {
/* 对齐方式 */
/* 左对齐 */
text-align: left;
}
.p4 {
/* 对齐方式 */
/* 两端对齐 */
text-align: justify;
}
装饰器
.p5 {
/* 装饰器 */
/* 下划线 */
text-decoration: underline;
}
.p6 {
/* 装饰器 */
/* 上划线 */
text-decoration: overline;
}
.p7 {
/* 装饰器 */
/* 删除线 */
text-decoration: line-through;
}
a {
/* 装饰器 */
/* 无装饰,一般用于a标签 */
text-decoration: none;
}
缩进
.p8 {
/* 缩进 */
/* 缩进两格 */
/*font-size: 16px;*/
/*text-indent: 32px;*/
text-indent: 2em;
}
代码演示
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<style>
.p1 {
/* 对齐方式 */
/* 居中 */
text-align: center;
}
.p2 {
/* 对齐方式 */
/* 右对齐 */
text-align: right;
}
.p3 {
/* 对齐方式 */
/* 左对齐 */
text-align: left;
}
.p4 {
/* 对齐方式 */
/* 两端对齐 */
text-align: justify;
}
.p5 {
/* 装饰器 */
/* 下划线 */
text-decoration: underline;
}
.p6 {
/* 装饰器 */
/* 上划线 */
text-decoration: overline;
}
.p7 {
/* 装饰器 */
/* 删除线 */
text-decoration: line-through;
}
a {
/* 装饰器 */
/* 无装饰,一般用于a标签 */
text-decoration: none;
}
.p8 {
/* 缩进 */
/* 缩进两格 */
/*font-size: 16px;*/
/*text-indent: 32px;*/
text-indent: 2em;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<p class="p1">奥特曼</p>
<p class="p2">奥特曼</p>
<p class="p3">奥特曼</p>
<p class="p4">奥特曼</p>
<p class="p5">奥特曼</p>
<p class="p6">奥特曼</p>
<p class="p7">奥特曼</p>
<a href="">点我</a>
<p class="p8">奥特曼123456</p>
<p class="p9">奥特曼123456</p>
</body>
</html>
演示结果

背景属性
<head>
<style>
div {
height: 1600px;
width: 1600px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="d1"></div>
</body>
背景颜色
.d1 {
background-color: yellowgreen;
}
背景图片
.d1 {
/* 默认平铺,即一定要填满区域 */
background-image: url("04-奥特曼.jpg");
/* 不平铺 */
/*background-repeat: no-repeat;*/
/* 浏览器坐标系是三维的,
X轴——水平方向
Y轴——垂直方向
Z轴——指向用户方向
*/
/* 沿 Y 轴 平铺,垂直方向 */
/*background-repeat: repeat-y;*/
/* 沿 X 轴 平铺,水平方向 */
background-repeat: repeat-x;
}
背景位置
.d1 {
/* position 只有两个参数,第一个参数是距离左的距离,第二个参数是距离上的距离,参数可以是负数 */
background-position: 100px 200px;
}
背景属性简写
.d1 {
/* 简写,参数没有顺序要求 */
background: url("04-奥特曼.jpg") yellowgreen no-repeat 100px 200px;
}
代码演示
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<style>
div {
height: 1600px;
width: 1600px;
}
/*.d1 {*/
/* background-color: yellowgreen;*/
/*}*/
/*.d1 {*/
/* !* 默认平铺,即一定要填满区域 *!*/
/* background-image: url("04-奥特曼.jpg");*/
/* !* 不平铺 *!*/
/* background-repeat: no-repeat;*/
/* !* 浏览器坐标系是三维的,*/
/* X轴——水平方向*/
/* Y轴——垂直方向*/
/* Z轴——指向用户方向*/
/* *!*/
/* !* 沿 Y 轴 平铺,垂直方向 *!*/
/* !*background-repeat: repeat-y;*!*/
/* !* 沿 X 轴 平铺,水平方向 *!*/
/* !*background-repeat: repeat-x;*!*/
/*}*/
/*.d1 {*/
/* !* position 只有两个参数,第一个参数是距离左的距离,第二个参数是距离上的距离,参数可以是负数 *!*/
/* background-position: 100px 200px;*/
/*}*/
.d1 {
/* 简写,参数没有顺序要求 */
background: url("04-奥特曼.jpg") yellowgreen no-repeat 100px 200px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="d1"></div>
</body>
</html>
演示结果

边框
普通写法
.d1 {
/* 边框,上下左右 */
/* 边框颜色 */
border-left-color: red;
/* 边框样式,实线 */
border-left-style: solid;
/* 边框宽度 */
border-left-width: 5px;
/* 上边框 */
border-top: ;
/* 下边框 */
border-bottom: ;
/* 右边框 */
border-right: ;
}
简写
.d1 {
/* 简写,参数也没有顺序 */
border: 3px red solid;
}
弧度设置
.d1 {
border: red 3px solid;
/* 弧度设置,设置为 50%,如果长宽一样,那么边框就是圆形,否则是椭圆 */
border-radius: 50%;
}
代码演示
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<style>
div {
height: 200px;
width: 200px;
}
/*.d1 {*/
/* !* 边框,上下左右 *!*/
/* !* 边框颜色 *!*/
/* border-left-color: red;*/
/* !* 边框样式,实线 *!*/
/* border-left-style: solid;*/
/* !* 边框宽度 *!*/
/* border-left-width: 5px;*/
/* !* 上边框 *!*/
/* border-top: ;*/
/* !* 下边框 *!*/
/* border-bottom: ;*/
/* !* 右边框 *!*/
/* border-right: ;*/
/*}*/
/*.d1 {*/
/* !* 简写,参数也没有顺序 *!*/
/* border: 3px red solid;*/
/*}*/
.d1 {
border: red 3px solid;
/* 弧度设置,设置为 50%,如果长宽一样,那么边框就是圆形,否则是椭圆 */
border-radius: 50%;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="d1"></div>
</body>
</html>
演示结果

display 属性
标签转化为块级标签 ,行内标签,行内块标签
代码演示
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<style>
.d1 {
/* 转换为行内标签 */
display: inline;
height: 200px;
width: 200px;
background-color: green;
}
.s1 {
/* 转化为块级标签 */
display: block;
height: 200px;
width: 200px;
background-color: red;
}
.s2 {
/* 既有块级元素的特征又有行内元素的特征 */
display: inline-block;
width: 200px;
background: yellow;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="d1">123456</div>
<span class="s1">123456</span>
<span class="s2">123456</span>
</body>
</html>
演示结果

盒子模型
margin 属性
以快递作类比,
快递盒与快递盒之间的距离,在 HTML 中表现为标签和标签之间的距离,即外边距,属性名为 margin
代码演示
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<style>
body {
/* 浏览器默认 body 自带 margin,所以我们一般先去除 body 的 margin*/
/* margin 0 表示上下左右外边距都是 0 */
margin: 0;
/*第一个上下 第二个左右*/
/*margin: 10px 20px;*/
/*第一个上,第二个左右,第三个下*/
/*margin: 10px 20px 30px;*/
/*上 右 下 左*/
/*margin: 10px 20px 30px 40px;*/
}
.d1 {
/* 上外边距 */
margin-top: 15px;
/* 下外边距 */
margin-bottom: 10px;
/* 左外边距 */
margin-left: 20px;
/* 右外边距 */
margin-right: 10px;
height: 200px;
width: 200px;
background-color: green;
}
.d2 {
/* 此时 d2 的 margin-top 是 d1 的 margin-bottom,浏览器在渲染时选择数值较大的那个作为外边距,即 d1 和 d2 的距离仍是 10px */
margin-top: 5px;
height: 200px;
width: 200px;
background-color: blue;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="d1"></div>
<div class="d2"></div>
</body>
</html>
演示结果
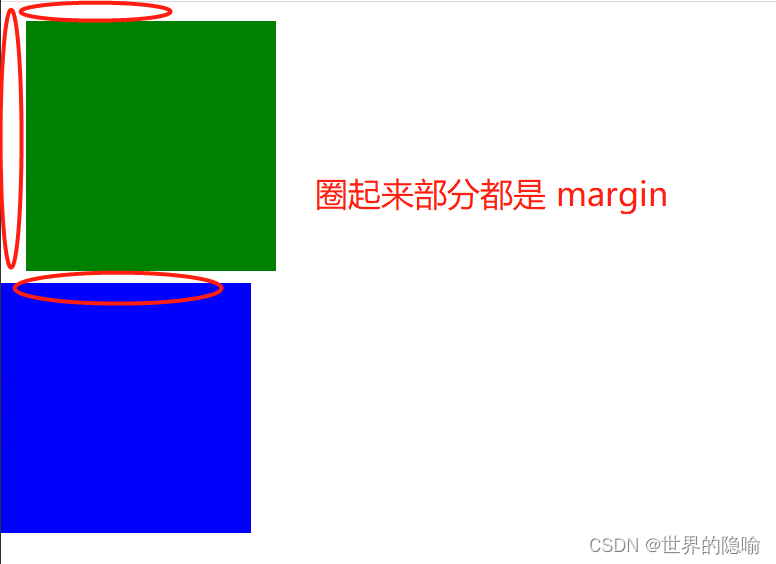
border 属性
快递盒的厚度,在 HTML 中表现为标签的边框,属性名为 border
padding 属性
快递盒内物体和快递盒之间的距离,即标签和标签内容之间的距离,属性名为 padding
代码演示
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<style>
span {
/* 简写和 margin 基本一致 */
padding-left: 15px;
padding-right: 5px;
padding-bottom: 20px;
padding-top: 10px;
}
.s1 {
background-color: green;
}
.s2 {
background-color: #3CA6FF;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<span class="s1">123</span>
<span class="s2">456</span>
</body>
</html>
演示结果
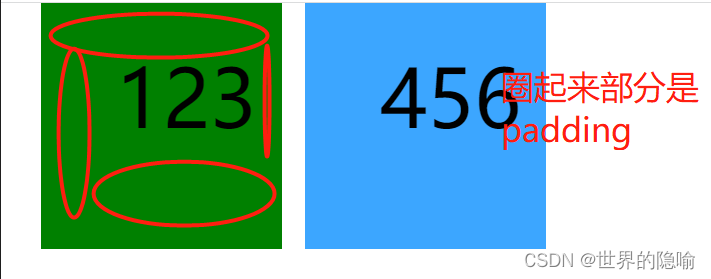
content 属性
快递盒内物品的大小,content
浮动
在写一个网页页面时,我们常常使用 div 标签占位,显然易见,我们会有两个 div 在一行的情况出现。这种情况我们可以用 display 的属性进行解决,但一般情况下,我们不考虑这种方式,而是选择浮动。
而且我们在实验时发现使用 display 实现 两个 div 在一行 会在两个 div 中出现 margin,使用浮动则不会有这种情况
代码演示
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<style>
.d1 {
height: 200px;
width: 200px;
background-color: blue;
/*display: inline-block;*/
/* 向左浮动 */
float: left;
}
.d2 {
height: 200px;
width: 200px;
background-color: red;
/*display: inline-block;*/
/* 向左浮动 */
float: left;
}
.d3 {
height: 200px;
width: 200px;
background-color: blue;
/* 向右浮动 */
float: right;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="d1"></div>
<div class="d2"></div>
<div class="d3"></div>
</body>
</html>
代码演示——display 和 浮动对比
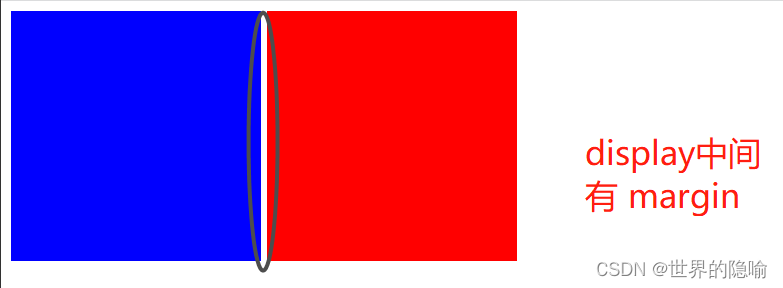

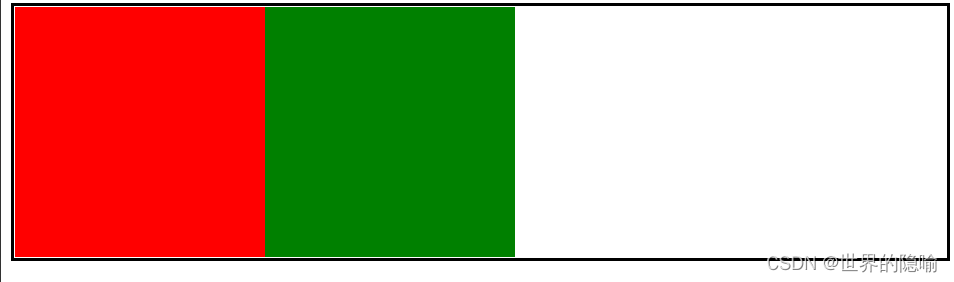
浮动带来的塌陷
浮动虽然很好用,但在使用过程中,浮动会造成父标签的塌陷——因为 div 的子标签浮动,所以父标签的 div 因为 没有设置长宽导致无法被撑开,上下边框直接重合。
塌陷演示
塌陷代码演示
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<style>
.d1 {
border: 3px black solid;
}
.d2 {
height: 200px;
width: 200px;
background-color: red;
float: left;
}
.d3 {
height: 200px;
width: 200px;
background-color: green;
float: left;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="d1">
<div class="d2"></div>
<div class="d3"></div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
塌陷演示结果

塌陷解决方法
解决方法
1. 在 父标签中添加一个和浮动的标签长宽相等的 子标签撑开父标签
2. 使用 clear 属性,作用是去除浮动
3. 通用方法,写一个 .clearfix:after 的 css,以后只要出现塌陷,就在 该标签的 class 中 添加该 类 就行了
代码演示
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<style>
.clearfix:after {
content: "";
display: block;
clear: both;
}
.d1 {
border: 3px black solid;
}
.d2 {
height: 200px;
width: 200px;
background-color: red;
float: left;
}
.d3 {
height: 200px;
width: 200px;
background-color: green;
float: left;
}
/*.d4 {*/
/* !*height: 200px;*!*/
/* !*width: 200px;*!*/
/* !* both 表示上下左右都清除浮动,除了 both,参数还可以是 top, left, right , bottom *!*/
/* !* left 表示只清楚左边浮动 *!*/
/* clear: left;*/
/*}*/
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="d1 clearfix">
<div class="d2"></div>
<div class="d3"></div>
<div class="d4"></div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
演示结果
定位
静态(static)
默认情况下,所有的网页标签都是静态的(static),没法改变位置
相对定位(relative)
相对于标签原来的位置进行移动(relative)
代码演示
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<style>
.d1 {
height: 200px;
width: 200px;
/* 相对定位 */
position: relative;
/* 自上而下移动 200px ,如果是负数,方向相反 */
top: 200px;
/* 自左向右,如果是负数,方向相反 */
left: 200px;
background-color: red;
}
body {
margin: 0;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="d1"></div>
</body>
</html>
演示结果
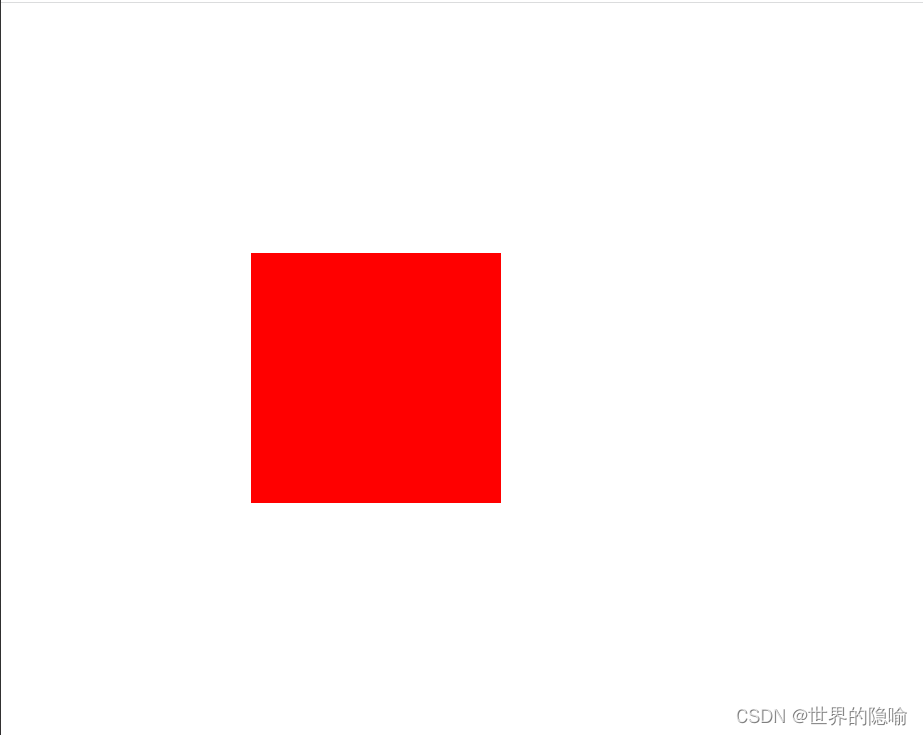
绝对定位(absolute)
相对于已经定位过的父标签位置进行移动,如果没有父标签,那么就以 body 为参照
eg. 小米购物车
代码演示
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<style>
body {
margin: 0;
}
.d2 {
height: 200px;
width: 200px;
background-color: green;
}
.d3 {
height: 100px;
width: 300px;
background-color: blue;
/* 绝对定位 */
position: absolute;
left: 200px;
top: 200px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="d2">
<div class="d3"></div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
演示结果
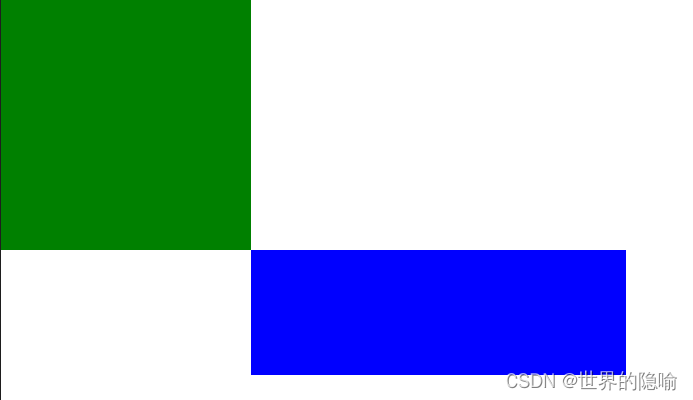
固定定位(fixed)
相对于浏览器固定在固定位置
eg.网站右侧导航栏(如:回到顶部)
代码演示
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<style>
body {
margin: 0;
}
.d4 {
height: 400px;
width: 800px;
}
.d5 {
height: 100px;
width: 100px;
/*border-radius: 50%;*/
border: 3px #4e4e4e solid;
color: #A00300;
/* 固定定位 */
position: fixed;
top: 200px;
left: 200px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="d4" style="background-color: red"></div>
<div class="d4" style="background-color: yellow"></div>
<div class="d4" style="background-color: green"></div>
<div class="d5">回到顶部</div>
</body>
</html>
浮动、定位是否脱离文档流
脱离文档流
移动后原位置被下面的标签所占据
不脱离文档流
相对定位
脱离文档流
浮动
绝对定位
固定定位
透明度 opacity
简单来说,opacity 调整不仅可以调整颜色透明度,还可以调整字体的透明度,而 rgba 只能调整颜色透明度
代码演示
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<style>
.d1 {
background-color: blue;
opacity: 0.5;
}
.d2 {
background-color: rgba(2, 2, 255, 0.5);
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="d1">111</div>
<div class="d2">222</div>
</body>
</html>
演示结果

溢出
溢出现象
有时候由于标签内部内容太长,而标签本身大小过小,导致在页面渲染展示时会造成内容仍然展示,但内容在标签外部的情况
代码演示
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<style>
p {
width: 100px;
height: 50px;
border: 3px black solid;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<p>12345612345612345612345612345612345612335</p>
</body>
</html>
演示结果
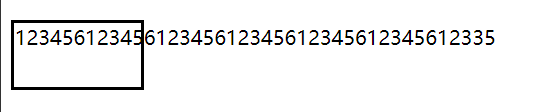
溢出解决方法
overflow 属性的使用
hidden:隐藏溢出部分
auto:自动,溢出部分滚动条
代码演示
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<style>
p {
width: 100px;
height: 50px;
border: 3px black solid;
/* 隐藏溢出部分 */
/*overflow: hidden;*/
/* 自动,溢出部分滚动条 */
overflow: auto;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<p>12345612345612345612345612345612345612335</p>
</body>
</html>
演示结果


溢出的应用
代码演示
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<style>
body {
margin: 0;
background-color: #4e4e4e;
}
div {
height: 200px;
width: 200px;
border-radius: 50%;
border: 3px white solid;
overflow: hidden;
margin: 0 auto;
}
div>img {
width: 100%;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div>
<img src="04-奥特曼.jpg" alt="头像">
</div>
</body>
</html>
演示结果

z-index 模态框
代码演示
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<style>
body {
margin: 0;
}
.cover {
background-color: rgba(0,0,0,0.5);
position: fixed;
left: 0;
right: 0;
top: 0;
bottom: 0;
/* 相当于z轴坐标为99,即更靠近用户 */
z-index: 99;
}
.modal {
width: 400px;
height: 200px;
background-color: white;
position: fixed;
top: 400px;
left: 400px;
/* 如果没有 z-index,modal 会被 cover 遮住,但由于浏览器优先展示文字内容,所以在运行时看起来像是颜色被遮住,事实上应该是全部被遮住 */
z-index: 100;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div>这是最底层</div>
<div class="cover"></div>
<div class="modal">
<h1>用户登录</h1>
<p>用户名
<input type="text">
</p>
<p>密码
<input type="password">
</p>
<button>点我</button>
</div>
</body>
</html>
演示结果




